3D Concrete printing Technology
What is 3D concrete printing?
3D concrete printing is a breakthrough technology that enables the creation of structural components and construction objects without the need for formwork. As a result, it allows the realization of complex non-linear architectures featuring smooth curves or unique spiral forms—designs that are very difficult to achieve using traditional construction methods.
This technology operates by depositing material layer by layer in a sequential manner under computer control. A 3D printer, consisting of either a robotic arm system or a gantry (Cartesian) system, moves the print head to precisely place concrete according to a pre-programmed design created in CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software.
See also: What is concrete? Everything you need to know about concrete
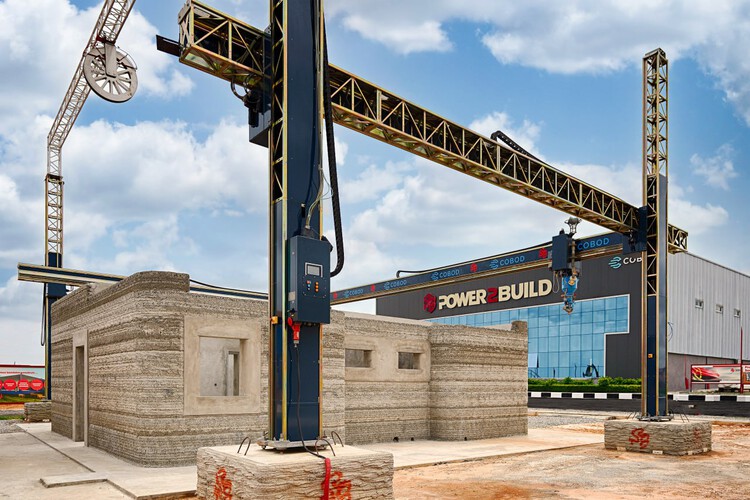

Advantages of 3D concrete printing technology
Thanks to its fundamentally different construction approach, 3D concrete printing not only overcomes the limitations of conventional construction methods but also offers many other outstanding benefits.
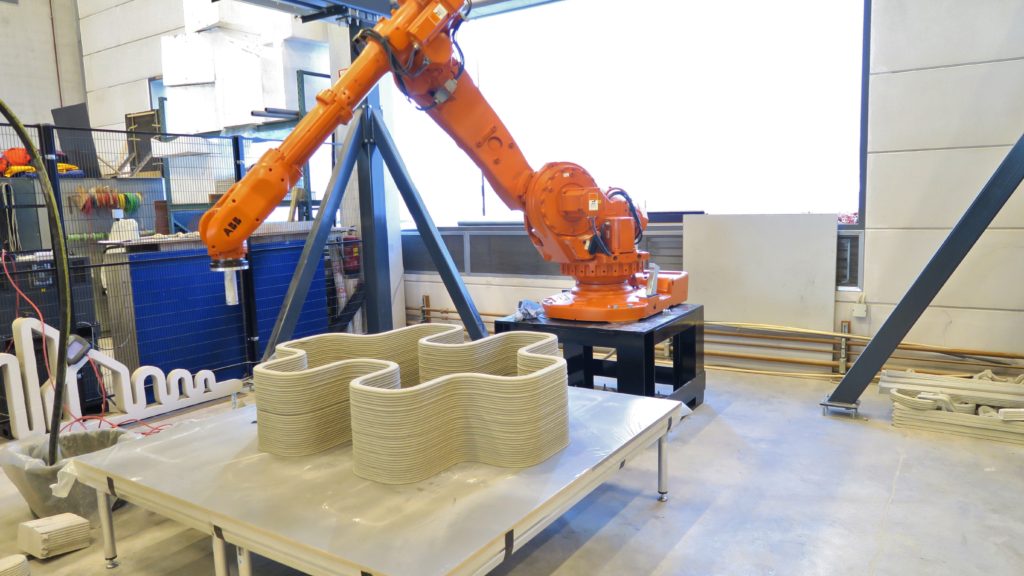
3D Concrete Printing Process
As a specialized technology, 3D concrete printing follows a construction process that differs significantly from traditional building methods.

Step 1 – Design and programming:
Engineers use 3D design software such as CAD to create a digital model of the structure. This model is then converted into a specialized file containing detailed instructions for the 3D printing robot, including tool paths, printing speed, and the amount of material to be extruded.
Step 2 – Material preparation:
Suitable 3D concrete printing material is mixed on-site or pre-produced, then fed into a pump system to ensure a continuous supply to the print head.
Step 3 – Printer setup:
The printer is installed, calibrated, and programmed according to the design, ensuring accuracy throughout the printing process.
Step 4 – 3D concrete printing execution:
The 3D printing robot extrudes successive layers of cementitious mortar from the bottom up, gradually “building” the pre-designed structure.
Step 5 – Finishing:
After printing, the structure undergoes surface treatment and the addition of elements such as doors, electrical systems, and plumbing before being put into use.
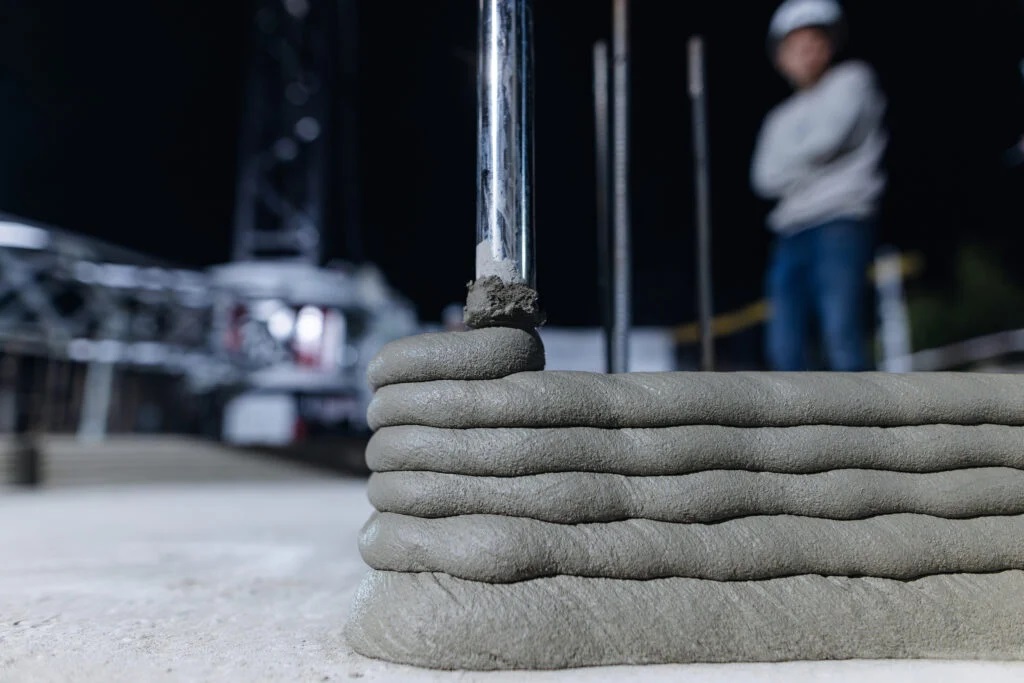

Materials for 3D Concrete Printing
3D printing does not use conventional Portland cement concrete. Instead, it relies on specialized materials that meet specific requirements to ensure stability, printability, and long-term durability of the structure.
-
Good pumpability and workability:
The material must have sufficient flowability to move smoothly through hoses and nozzles without clogging, while not being too fluid to avoid segregation. -
Strong interlayer adhesion:
Adequate cohesiveness allows layers to bond together without collapse. This is a key factor affecting structural stability, geometry, and the height of printed elements. -
Rapid setting time:
The material must harden quickly after extrusion to support the weight of subsequent layers, maintain shape, and minimize deformation. -
High strength:
Ensures the durability and service life of the structure. -
Reduced shrinkage:
Limits cracking, especially when printed layers are exposed to the external environment.
Meeting these technical requirements, Nafufill KM 250 is an ideal material for 3D concrete printing technology, particularly for mortar spraying methods. With compressive strength comparable to concrete, optimal density for easy application and shape retention, and enhanced resistance to carbonation and chloride penetration, Nafufill KM 250 provides outstanding durability for 3D-printed components even under harsh environmental conditions.
- Using AI for English Speaking Comprehension and Real-life
- Con đường giải mã suy nghĩ: từ ý niệm trong não đến chữ viết
- BẢO MẬT THÔNG TIN TRONG MẠNG TRUYỀN THÔNG KHÔNG DÂY
- [THÔNG BÁO] – Danh sách Đồ án Capstone 1&2 (Đợt tháng 01/2025)
- Phương pháp điều hành kinh doanh trên toàn cầu của IKEA và vai trò của văn hóa tổ chức



